Copyright © Shenzhen Yuanjingang New Materials Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Site Map
- 0086-400-9207007
- hemengzhu@weihaijiuhua.cn
- No. 17, Jinshaling Industrial Park, Weihai City, Shandong Province

In recent years, research on radiative cooling coatings has made significant progress. On the one hand, researchers have enhanced the cooling effect and stability of radiative cooling coatings by continuously optimizing the microstructure and composition of the materials . On the other hand, with the continuous development of nanotechnology, researchers have begun exploring the application of nanomaterials in radiative cooling coatings to enhance their performance and application range.

Yuanjingang radiant cooling and cooling coatings are all composite structures mainly composed of water-based inorganic ceramics. They have the advantages of being green and environmentally friendly, resistant to UV aging, highly flame retardant, low cost, and having a wide range of applications. They can be widely used in power communication cabinets, large building surfaces and roofs, oil storage tanks, grain warehouses and other fields, providing users with a long-lasting zero-energy cooling and energy-saving experience.
In response to the needs of different fields, radiant cooling coatings have been carefully developed to meet customer needs: ordinary water-based radiant cooling coatings, super-amphiphobic radiant cooling coatings, colored radiant cooling coatings, radiant cooling films and other series.
All series of products can be used in agriculture, construction, communications electronics, light industry and other fields.
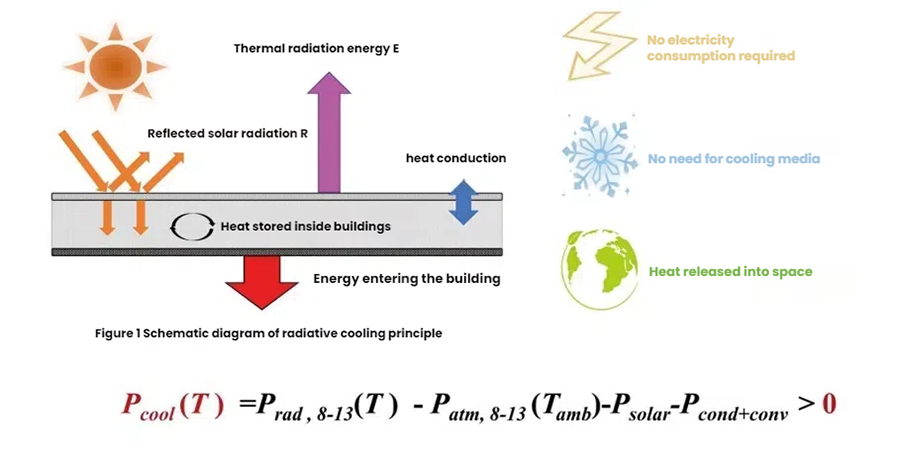
1. The basic principle of Yuanjingang radiant cooling coating
Yuanjingang Radiant Cooling Coating utilizes the thermal radiation properties of specialized materials to achieve a cooling effect. This coating reduces temperatures without consuming any energy. The principle is shown in Figure 1. This coating emits heat away from the Earth via infrared waves in the 8-13μm range, reflecting the vast majority of solar radiation. Ultimately, this reduces heat dissipation to a level greater than heat gain, resulting in a cooling power rating greater than zero, thus achieving cooling.
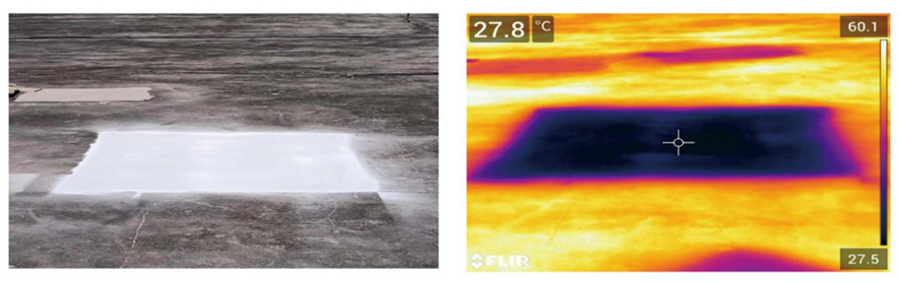
Yuanjingang radiant cooling coatings achieve significant surface cooling by combining high reflectivity and high radiation. The following figure shows the surface temperature change after the radiant cooling coating is applied.
2. Advantages of Radiant Cooling Coatings
High efficiency and energy saving: Radiant cooling coatings do not require external energy supply and achieve cooling through natural thermal radiation, so they have extremely low energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Environmentally friendly and pollution-free: Since no electricity or refrigerants are required, radiant cooling paint does not produce any pollutants during use and is environmentally friendly.
Widely applicable: Radiant cooling coatings can be used in many fields such as construction, automobiles, aerospace, etc., and have a wide range of applicability.
3. Future Prospects of Radiant Cooling Coatings
Yuanjingang's super-amphiphobic radiative cooling coating is a composite structure primarily composed of water-based inorganic ceramics. Its surface is hydrophobic and oleophobic, enabling the coating to simultaneously deliver radiative cooling capabilities while maintaining self-cleaning properties. This effectively prevents the deposition of airborne dust, moisture, rain-induced mud, and oil stains on the coating surface, significantly reducing maintenance and operating costs for equipment and walls in harsh conditions. Its environmentally friendly, acid- and alkali-resistant properties, combined with its wide range of applications, make it suitable for a wide range of applications, including power and telecommunications cabinets, large building surfaces and roofs, oil storage tanks, and grain depots.

With the continuous advancement of technology and the expansion of its application areas, radiative cooling coatings have broad prospects for future development. First, in the construction field, radiative cooling coatings can be applied to exterior walls, roofs, and other areas, effectively reducing a building's energy consumption and carbon emissions. Second, in the aerospace field, radiative cooling coatings can be used in the thermal control systems of equipment such as spacecraft and satellites, improving their thermal stability and service life. Furthermore, radiative cooling coatings can be applied to solar cells, power plant condensers, and other areas to improve energy efficiency.